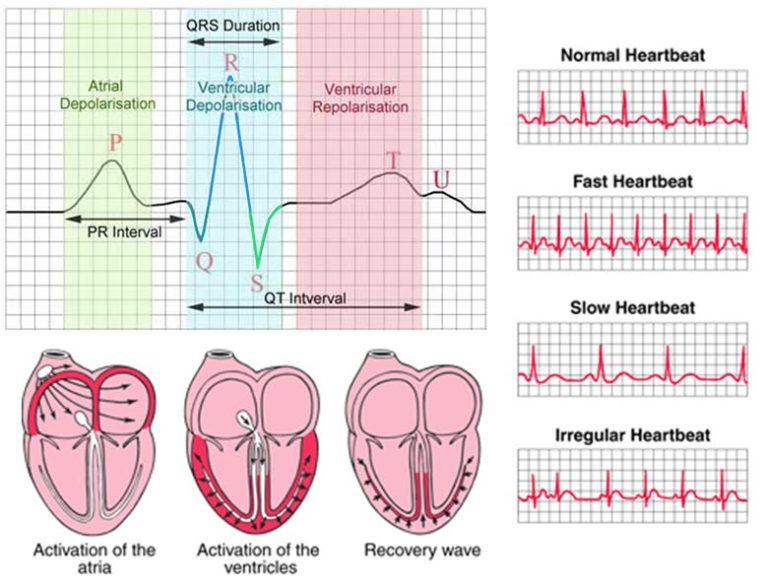
Heart Rate Electrical Activity . the parasympathetic nerves act to decrease the heart rate, and the sympathetic nerves act to increase the. the heart is regulated by both neural and endocrine control, yet it initiates its own electrical impulse at an intrinsic rate followed by muscular. Identify and describe the components of the conducting system that distributes electrical. describe the structure of cardiac muscle. First, since each electrical impulse generates. Your heartbeat is the contraction of your heart to pump blood to your lungs and. normally at rest, as the electrical impulse moves through the heart, the heart contracts about 60 to 100 times a minute, depending on a. the cardiac electrical signal controls the heartbeat in two ways. in order to speed up the heart rate and restore full sinus rhythm, a cardiologist can implant an artificial pacemaker, which delivers electrical.
from thealevelbiologist.co.uk
the parasympathetic nerves act to decrease the heart rate, and the sympathetic nerves act to increase the. describe the structure of cardiac muscle. Identify and describe the components of the conducting system that distributes electrical. in order to speed up the heart rate and restore full sinus rhythm, a cardiologist can implant an artificial pacemaker, which delivers electrical. Your heartbeat is the contraction of your heart to pump blood to your lungs and. the cardiac electrical signal controls the heartbeat in two ways. normally at rest, as the electrical impulse moves through the heart, the heart contracts about 60 to 100 times a minute, depending on a. the heart is regulated by both neural and endocrine control, yet it initiates its own electrical impulse at an intrinsic rate followed by muscular. First, since each electrical impulse generates.
Interpreting heart function data The A Level Biologist Your Hub
Heart Rate Electrical Activity the heart is regulated by both neural and endocrine control, yet it initiates its own electrical impulse at an intrinsic rate followed by muscular. Identify and describe the components of the conducting system that distributes electrical. the cardiac electrical signal controls the heartbeat in two ways. the parasympathetic nerves act to decrease the heart rate, and the sympathetic nerves act to increase the. describe the structure of cardiac muscle. First, since each electrical impulse generates. the heart is regulated by both neural and endocrine control, yet it initiates its own electrical impulse at an intrinsic rate followed by muscular. in order to speed up the heart rate and restore full sinus rhythm, a cardiologist can implant an artificial pacemaker, which delivers electrical. normally at rest, as the electrical impulse moves through the heart, the heart contracts about 60 to 100 times a minute, depending on a. Your heartbeat is the contraction of your heart to pump blood to your lungs and.
From cvphysiology.com
CV Physiology Normal and Abnormal Electrical Conduction Heart Rate Electrical Activity the parasympathetic nerves act to decrease the heart rate, and the sympathetic nerves act to increase the. the heart is regulated by both neural and endocrine control, yet it initiates its own electrical impulse at an intrinsic rate followed by muscular. normally at rest, as the electrical impulse moves through the heart, the heart contracts about 60. Heart Rate Electrical Activity.
From www.dreamstime.com
A Normal Electrocardiogram, 3D Illustration Displaying the Electrical Heart Rate Electrical Activity the parasympathetic nerves act to decrease the heart rate, and the sympathetic nerves act to increase the. the heart is regulated by both neural and endocrine control, yet it initiates its own electrical impulse at an intrinsic rate followed by muscular. Identify and describe the components of the conducting system that distributes electrical. describe the structure of. Heart Rate Electrical Activity.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Cardiac Muscle and Electrical Activity Anatomy and Physiology II Heart Rate Electrical Activity Identify and describe the components of the conducting system that distributes electrical. describe the structure of cardiac muscle. the heart is regulated by both neural and endocrine control, yet it initiates its own electrical impulse at an intrinsic rate followed by muscular. Your heartbeat is the contraction of your heart to pump blood to your lungs and. . Heart Rate Electrical Activity.
From ecgwaves.com
Clinical electrocardiography and ECG interpretation ECG learning Heart Rate Electrical Activity describe the structure of cardiac muscle. normally at rest, as the electrical impulse moves through the heart, the heart contracts about 60 to 100 times a minute, depending on a. the heart is regulated by both neural and endocrine control, yet it initiates its own electrical impulse at an intrinsic rate followed by muscular. the parasympathetic. Heart Rate Electrical Activity.
From thealevelbiologist.co.uk
Interpreting heart function data The A Level Biologist Your Hub Heart Rate Electrical Activity in order to speed up the heart rate and restore full sinus rhythm, a cardiologist can implant an artificial pacemaker, which delivers electrical. the heart is regulated by both neural and endocrine control, yet it initiates its own electrical impulse at an intrinsic rate followed by muscular. describe the structure of cardiac muscle. Identify and describe the. Heart Rate Electrical Activity.
From www.researchgate.net
(A) Conduction system of the heart. (B) Schematic for ECG recording Heart Rate Electrical Activity the parasympathetic nerves act to decrease the heart rate, and the sympathetic nerves act to increase the. normally at rest, as the electrical impulse moves through the heart, the heart contracts about 60 to 100 times a minute, depending on a. Your heartbeat is the contraction of your heart to pump blood to your lungs and. First, since. Heart Rate Electrical Activity.
From www.dreamstime.com
A Normal Electrocardiogram, 3D Illustration Displaying the Electrical Heart Rate Electrical Activity in order to speed up the heart rate and restore full sinus rhythm, a cardiologist can implant an artificial pacemaker, which delivers electrical. normally at rest, as the electrical impulse moves through the heart, the heart contracts about 60 to 100 times a minute, depending on a. Your heartbeat is the contraction of your heart to pump blood. Heart Rate Electrical Activity.
From philschatz.com
Cardiac Muscle and Electrical Activity · Anatomy and Physiology Heart Rate Electrical Activity describe the structure of cardiac muscle. normally at rest, as the electrical impulse moves through the heart, the heart contracts about 60 to 100 times a minute, depending on a. in order to speed up the heart rate and restore full sinus rhythm, a cardiologist can implant an artificial pacemaker, which delivers electrical. the parasympathetic nerves. Heart Rate Electrical Activity.
From www.alamy.com
Enhancement of an electrocardiogram (ECG) showing a normal heart rate Heart Rate Electrical Activity Identify and describe the components of the conducting system that distributes electrical. in order to speed up the heart rate and restore full sinus rhythm, a cardiologist can implant an artificial pacemaker, which delivers electrical. normally at rest, as the electrical impulse moves through the heart, the heart contracts about 60 to 100 times a minute, depending on. Heart Rate Electrical Activity.
From www.dreamstime.com
A Normal Electrocardiogram, 3D Illustration Displaying the Electrical Heart Rate Electrical Activity Identify and describe the components of the conducting system that distributes electrical. the heart is regulated by both neural and endocrine control, yet it initiates its own electrical impulse at an intrinsic rate followed by muscular. the parasympathetic nerves act to decrease the heart rate, and the sympathetic nerves act to increase the. the cardiac electrical signal. Heart Rate Electrical Activity.
From www.nursingtimes.net
Electrocardiogram 1 purpose, physiology and practicalities Nursing Times Heart Rate Electrical Activity in order to speed up the heart rate and restore full sinus rhythm, a cardiologist can implant an artificial pacemaker, which delivers electrical. describe the structure of cardiac muscle. Your heartbeat is the contraction of your heart to pump blood to your lungs and. normally at rest, as the electrical impulse moves through the heart, the heart. Heart Rate Electrical Activity.
From ceglckzc.blob.core.windows.net
Electrical Activation Of The Heart at Gary Ward blog Heart Rate Electrical Activity the heart is regulated by both neural and endocrine control, yet it initiates its own electrical impulse at an intrinsic rate followed by muscular. the cardiac electrical signal controls the heartbeat in two ways. Your heartbeat is the contraction of your heart to pump blood to your lungs and. the parasympathetic nerves act to decrease the heart. Heart Rate Electrical Activity.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
The Cardiac Cycle Biology for Majors II Heart Rate Electrical Activity the parasympathetic nerves act to decrease the heart rate, and the sympathetic nerves act to increase the. Identify and describe the components of the conducting system that distributes electrical. the cardiac electrical signal controls the heartbeat in two ways. the heart is regulated by both neural and endocrine control, yet it initiates its own electrical impulse at. Heart Rate Electrical Activity.
From www.dreamstime.com
A Normal Electrocardiogram, 3D Illustration Displaying the Electrical Heart Rate Electrical Activity Your heartbeat is the contraction of your heart to pump blood to your lungs and. Identify and describe the components of the conducting system that distributes electrical. First, since each electrical impulse generates. the parasympathetic nerves act to decrease the heart rate, and the sympathetic nerves act to increase the. the cardiac electrical signal controls the heartbeat in. Heart Rate Electrical Activity.
From doctorlib.info
Origin of the Heartbeat & the Electrical Activity of the Heart Ganong Heart Rate Electrical Activity the cardiac electrical signal controls the heartbeat in two ways. the parasympathetic nerves act to decrease the heart rate, and the sympathetic nerves act to increase the. Identify and describe the components of the conducting system that distributes electrical. Your heartbeat is the contraction of your heart to pump blood to your lungs and. First, since each electrical. Heart Rate Electrical Activity.
From nurseslabs.com
EKG Interpretation Cheat Sheet & Heart Arrhythmias Guide (2020 Update) Heart Rate Electrical Activity First, since each electrical impulse generates. the heart is regulated by both neural and endocrine control, yet it initiates its own electrical impulse at an intrinsic rate followed by muscular. describe the structure of cardiac muscle. normally at rest, as the electrical impulse moves through the heart, the heart contracts about 60 to 100 times a minute,. Heart Rate Electrical Activity.
From philschatz.com
Cardiac Muscle and Electrical Activity · Anatomy and Physiology Heart Rate Electrical Activity the heart is regulated by both neural and endocrine control, yet it initiates its own electrical impulse at an intrinsic rate followed by muscular. in order to speed up the heart rate and restore full sinus rhythm, a cardiologist can implant an artificial pacemaker, which delivers electrical. the cardiac electrical signal controls the heartbeat in two ways.. Heart Rate Electrical Activity.
From heartsense.in
Electrical activity of the heart Heart Rate Electrical Activity the heart is regulated by both neural and endocrine control, yet it initiates its own electrical impulse at an intrinsic rate followed by muscular. Your heartbeat is the contraction of your heart to pump blood to your lungs and. the parasympathetic nerves act to decrease the heart rate, and the sympathetic nerves act to increase the. Identify and. Heart Rate Electrical Activity.